Deny
climate change all you want, but just get used to a bumpy ride. A really
bumpy airplane ride, that is:
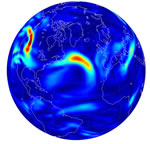
For their analysis, they simulated atmospheric conditions at an altitude
of about 12 kilometers (a typical cruise altitude for airliners) in
the northern portion of the North Atlantic, a region that includes most
transatlantic routes. During winter months, when clear-air turbulence
is at its worst in that area, 16 of the 21 often-used ways in which
scientists measure turbulence suggest that the
average intensity of the plane-rattling phenomenon (image depicts turbulence
intensity on a random winter day) will be between 10% and 40% stronger
when CO2 concentrations are double their preindustrial value, the
researchers report online today in Nature Climate Change. Accordingly,
the frequency of moderate-or-greater turbulence—intensities at
which passengers will experience accelerations of 0.5 g or more, which
are strong enough to toss items about the cabin—will rise by between
40% and 170%.
 Deny
climate change all you want, but just get used to a bumpy ride. A really
bumpy airplane ride, that is:
Deny
climate change all you want, but just get used to a bumpy ride. A really
bumpy airplane ride, that is:
No comments:
Post a Comment